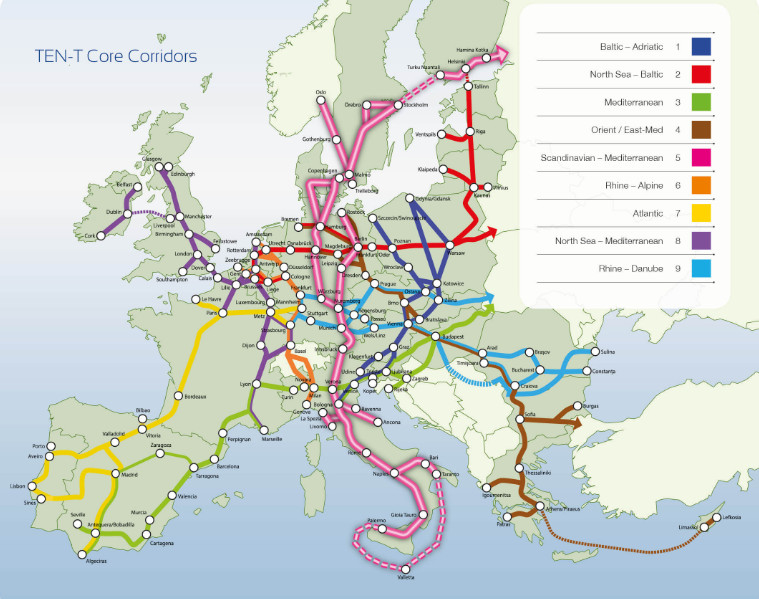
The Trans-European Transport Network (TEN-T) is a vast network of infrastructure for transport in the European Union (EU) that aims to connect people and businesses throughout the continent by improving the flow of goods, services, and passengers. The TEN-T covers all modes of transport, including road, rail, water, and air, and is intended to support economic growth, enhance social cohesion, and promote sustainable mobility. In this article, we will take a closer look at the TEN-T, its objectives, and its impact on the EU.
Overview of the Trans-European Transport Network
The TEN-T was established in 1996 as part of the EU’s efforts to create a single market for transport in Europe. The network comprises a series of corridors that connect EU member states and neighboring countries, with a total length of over 92,000 kilometers for road and rail transport, over 43,000 kilometers for inland waterways, and more than 27,000 kilometers for maritime transport.
The corridors of the TEN-T are designed to provide seamless transport connections across Europe, with a focus on intermodality and multimodality. The network is also intended to enhance the efficiency and safety of transport operations and to promote sustainable mobility through the use of new technologies, alternative fuels, and the reduction of emissions.
Objectives of the Trans-European Transport Network
The TEN-T has several objectives that are aimed at improving the transport infrastructure and services in the EU. These objectives include:
- Connecting regions: The TEN-T aims to connect regions and countries that are geographically and economically distant from each other, thereby reducing disparities and promoting economic and social cohesion.
- Removing bottlenecks: The network seeks to eliminate bottlenecks in the transport system, such as missing links, congestion, and capacity constraints, that hinder the flow of goods, services, and passengers.
- Improving interoperability: The TEN-T aims to enhance the interoperability of different transport modes and systems, enabling smooth and efficient transfers between them.
- Ensuring safety and security: The network strives to improve the safety and security of transport operations by implementing common standards, regulations, and procedures.
- Promoting sustainability: The TEN-T aims to promote sustainable mobility by reducing the environmental impact of transport operations, encouraging the use of alternative fuels and modes of transport, and promoting the deployment of new technologies.
Impact of the Trans-European Transport Network
The TEN-T has had a significant impact on the transport infrastructure and services in the EU since its establishment. The network has facilitated the movement of goods, services, and passengers across borders and regions, boosting economic growth and trade.
The TEN-T has also helped to reduce the disparities between the EU member states and regions by providing better transport connections to less-developed areas. The network has also supported the growth of the EU’s internal market, enabling businesses to access new markets and customers.
Moreover, the TEN-T has contributed to the development of new technologies and innovative solutions for transport, such as intelligent transport systems, alternative fuels, and intermodal transport. The network has also played a crucial role in improving the environmental performance of transport operations, promoting sustainable mobility, and reducing the EU’s dependence on fossil fuels.
Challenges and Future of the Trans-European Transport Network
Despite its achievements, the TEN-T still faces several challenges that need to be addressed in the future. One of the main challenges is the lack of funding and investment for the network’s development and maintenance. The EU and the member states need to ensure sufficient funding and resources to complete the planned infrastructure projects and to maintain the existing transport network.
Another challenge is the need for greater coordination and cooperation between the EU and its neighboring countries to ensure the seamless flow of goods, services, and passengers across borders. The TEN-T needs to be integrated with the transport infrastructure and networks of the EU’s neighbors to the east and south, such as the Western Balkans, the Eastern Partnership countries, and the countries of the Southern Neighborhood.
The TEN-T also needs to address the challenges posed by the rapid technological advancements in transport, such as the rise of autonomous vehicles, the development of new fuels and propulsion systems, and the emergence of digital platforms for mobility services. The network needs to adapt to these changes and ensure that its infrastructure and services are future-proof and resilient.
Looking to the future, the TEN-T is expected to play a crucial role in achieving the EU’s long-term goals for transport, such as the decarbonization of transport, the digitalization of mobility services, and the promotion of sustainable and smart mobility. The network will also be a key driver of the EU’s recovery and resilience, supporting the post-pandemic economic growth and job creation.
Conclusion
The Trans-European Transport Network is a vital infrastructure for transport in the EU that connects people, businesses, and regions across the continent. The network has contributed to the economic, social, and environmental development of the EU since its establishment and has helped to reduce disparities between member states and regions.
However, the TEN-T still faces several challenges, such as the need for more funding and investment, greater cooperation with neighboring countries, and the adaptation to new technological trends. Nevertheless, the network remains a crucial element of the EU’s transport policy and a key driver of its sustainable and smart mobility agenda.
In 2022 Ukraine’s logistics routes have become part of the Trans-European Transport Network.